Getting ready for mobile app development? You wonder what technology to choose and how this choice may affect your long-term strategy? This article will help you learn about the pros and cons of native mobile apps and those made using React Native. It will also help you decide which technology is right for employing in a given situation and how a bad choice can influence your company’s future.
What is React Native
React Native is a cross-platform framework created and developing by Facebook. It allows creating Android and iOS apps using JavaScript. Thanks to React Native layout components developers can create user interfaces that are indistinguishable from those written in native technologies. React Native enables programmers to share the code between two platforms thanks to its ability to “translate” JavaScript into native components using so-called “bridges”, hence the name — React Native.
Pros of React Native in comparison to native technologies
React Native was created to accelerate the development process of mobile applications, save resources and enable organizations to move faster thanks to its several features listed below.
Faster development process
This is the biggest advantage of React Native. Thanks to “hot reloading” feature developers save time spent on code compilation which takes longer when using native programming languages. Changes made in code can be visible within seconds not minutes as is in case of native technologies.
Cross-platform code sharing → money saving
React Native allows to share about 70% of a codebase, depending on how advanced the app is and on platform-specific component usage. The more of this components the less code can be shared. If you keep the app simple you can use more shared code.
Better than hybrid apps
React Native framework is not a hybrid technology (like Cordova, Ionic, etc.) that uses so-called WebView which is a set of web components placed in mobile apps. Such a solution does not enable to employ native UI as well as use some of a mobile device capabilities available via API. React Native allows developers to use native interface components and quite a few platform-specific APIs.
Cons of React Native in comparison to native technologies
Despite its advantages, React Native has several flaws that mainly come out during mobile app development. Furthermore, many problems encountered when using this technology are a result of RN’s immaturity.
You have to use native code anyway
As mentioned before, to create specific parts of a mobile app you’ll have to use native code. Modules responsible for supporting unique smartphone features (e.g. camera or accelerometer) have to be written using native technologies. Yes, you can leverage 3rd party libraries, but that’s not the same as Facebook support. Thus, for some functions you will have to use native technologies anyway. You’ll also have to develop so-called “bridges” to link JavaScript components with native ones.
React Native does not support native APIs and SDKs
Despite constant advancement of RN technology, it does not provide ready-to-use modules that give access to iOS or Android APIs. This forces developers to create so-called Native Modules themselves or develop “bridges” using Java/Kotlin (Android) or Swift/Objective-C (iOS) and severely increases software development time. Native technologies require no such thing.
The same goes for native frameworks, libraries or SDKs — if you want to employ Augmented Reality, voice assistants or SDK for mobile payments, again, you’ll need the aforementioned bridges. This will require you to hire three developers instead of two as it was in the case of Airbnb that had to learn about it the hard way.
Performance
Using the aforementioned bridges or Native Modules instead of native APIs has a negative impact on mobile app performance. That is why many companies (including Airbnb or Udacity) turn away from RN. Apart from the above, the fact that smartphone processors and memory are set for supporting native components may also affect device performance.
Longer debugging
Developers bring up one more problem with React Native technology — software debugging. It is much harder when using RN. It comes down to faster development but longer problem-solving which results in less accurate cost estimation (especially in case of Android).
Facebook…
As we stated at the beginning, React Native was created by Facebook which is responsible for the further development of this framework. There’s always a chance that Facebook will abandon RN thus stopping its development. It is not very likely but we all know that corporations can be quite unpredictable. But the biggest threat is that Facebook can retract their permission to use this technology if they decide that your project violates their rules.
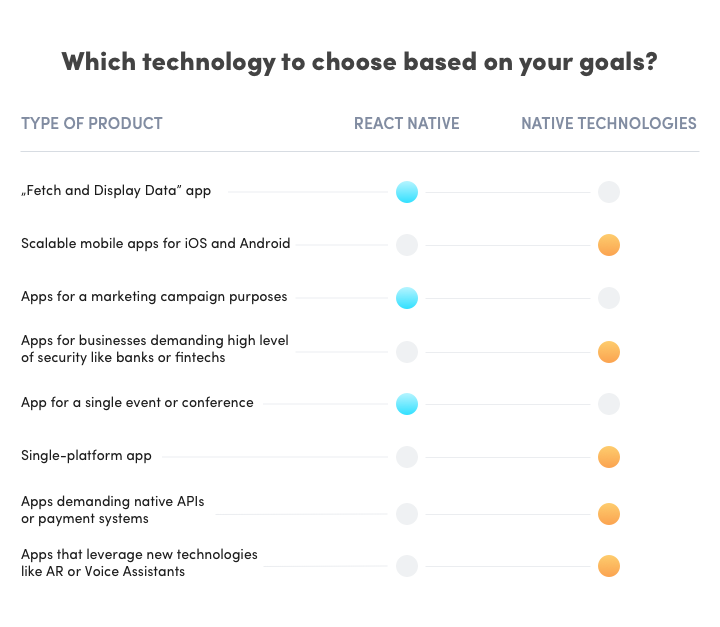
Which technology to choose based on your strategy?
Whatever choice you make in terms of technology it should be based on your goals and strategy and never the other way around. Don’t allow the technology to negatively impact or limit your strategy. Think about the goals, time perspective in which you’ll be employing your solution and how you plan on using unique mobile device features.
If you are still wondering how to get to creating mobile application software take a look at the manual that we’ve prepared for you. But right now let us advise you on when to use React Native and when it’s best to choose native technologies.
When you should use React Native
Over the last few years (RN was created in 2015) React Native gained popularity thanks to being a short-term “half measure” that enabled to create mobile apps for both Android and iOS platforms, allowing both versions to share most of the code at the same time. As of today, most companies treat this solution as a measure that best serves them when they need apps for certain events or short-term campaigns — software that does not perform complicated functions and its lifespan is relatively short.
React Native is based on JavaScript which is one of the most widely used programming languages. That is why if you develop a web product and want to create a simple mobile app for viewing data (like “Fetch and Display Data”) you can do it using your in-house team. In this case it would be more effective to use React.js developers than hire mobile developers.
Remember — do not use RN when you are designing a single-platform app. This framework was created to optimise multi-platform product development process and you will not benefit from using it when you aim for only one.
When you should use native mobile technology
Arguments for native mobile technologies are related to the future of your product — we believe that for long-term projects native apps are the best choice.
If your goal is to implement big, stable application software that is to be further developed in the future then React Native is not the best choice. It’s because while you can create a lot of code that is shared between two platforms it will still only be about 70% and in case of native apps you’ll also need a “bridge” between JavaScript and native code.
The simpler the app (e.g. “Fetch and Display Data” software), and the more generic the interface, the more code can be shared between platforms. By the same logic the more complicated the features, and peculiar the interface components, the more native code and “duct tape” is needed. The same goes for dependencies on outer, native libraries, like in case of reading QR codes, native APIs or payment systems.
If you are planning to use:
- OCR to recognize shipment numbers and fill in proper fields for the users
- Tools employing AR
- Voice assistants
Remember that in the above cases only native apps will be able to fully support the mentioned technologies. It basically comes down to this that if an interesting feature is designed for a given platform (e.g. ARKit for iOS) there is no telling when the necessary technology will be adapted in RN.
The future of React Native
The increasing demand for faster app development might be the reason why cross-platform applications are on the rise. In fact, React Native is already perceived as a viable solution to create quality software and its use is expected to grow in the coming years. Given the support of both community and tech giants, this trend is hardly surprising – especially since the framework has gained enormous popularity and community support in just a few years.
With Facebook having big plans for the framework (as mentioned in its State of React Native 2018), the future of React Native seems bright. Yet, not everyone agrees that it’s the way forward for mobile app development. And rightly so – there are still some technical drawbacks that are holding React Native back, not to mention that it generally offers slower apps when comparing them with native solutions.
The framework might look strong on paper, but many well-known apps (such as Airbnb or Udacity) has actually switched back to native development. Therefore, even though React Native is definitely a trending topic at the moment, only time will tell if it has the power to outshine native technologies.
Summary
The golden rule when choosing technology is to select a solution that will support your goals and strategy. Therefore, if your goal is to create a simple mobile app that will serve marketing purposes, will be used on a single event and not continued after that then definitely choose React Native — you’ll save time and money.
But if your app will be a part of your long-term strategy and you want to further develop it in the future, especially by using payment systems for e-commerce purposes, Augmented Reality, Voice Assistants, etc., choose native technologies — in the long run they’ll prove to be the most effective.
Want to build a reliable application but don’t know where to start? Don’t hesitate to book a free consultation. We’re always happy to help!